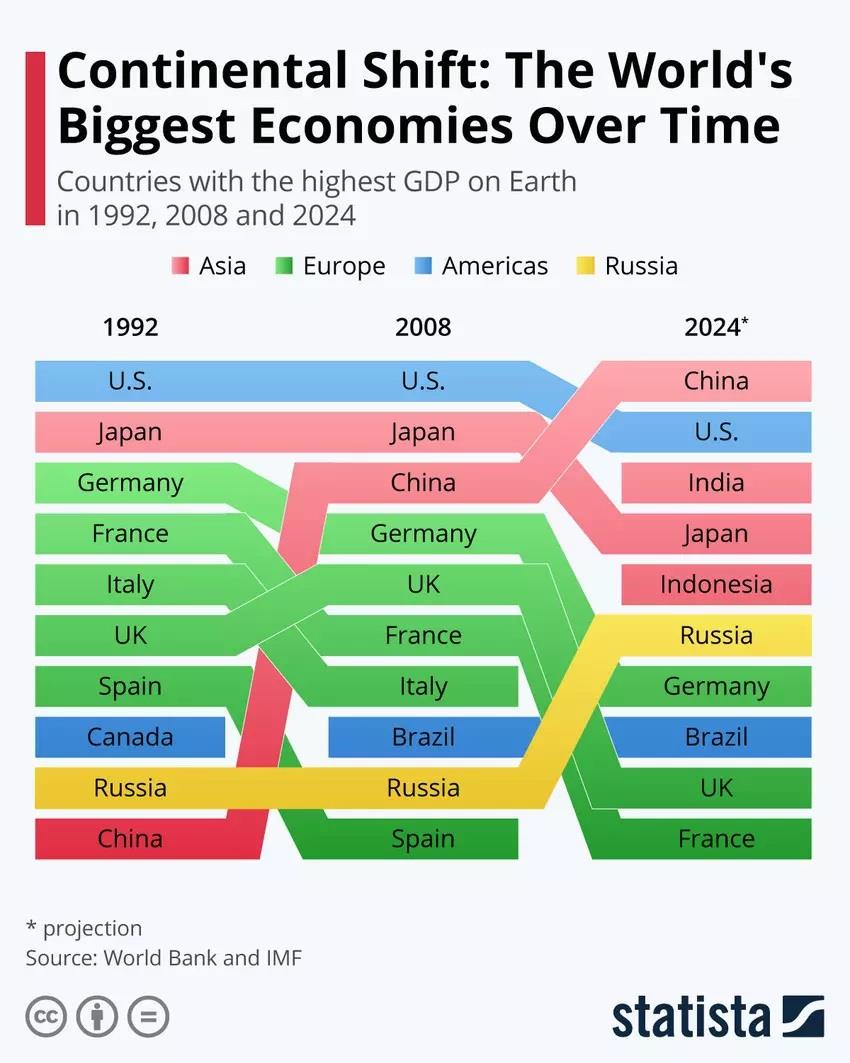
SWITZERLAND, Dec. 26 (World Economic Forum) - According to data from the World Bank and IMF, Asian countries are expected to make up most of the top 5 countries in the world by size of GDP in 2024, relegating European economic powerhouses to lower ranks.
China's economic growth has been steep since the 1990s, while India and Indonesia have even more recently entered the top 10 of the biggest economies in the world and are expected to reach ranks 3 and 5 by 2024. Japan, an established economy, is expected to cling on to rank 4 in 2024, while Russia will rise to rank 6.
Asia’s burgeoning middle class is one of the reasons for the continental shift in GDP. While China has been the posterchild of market growth in the 21st century so far, the country is expected to tackle an ageing population further down the line, which will put a damper on consumption. Indonesia, together with the Philippines and Malaysia, are expected to grow their labor forces significantly in the years to come, contributing to a rise in average disposable incomes, according to the World Economic Forum.
Asian multinationals, like China’s Huawei and India’s Tata, have already emerged in this century and more are expected to appear on the global scene. But rapid growth in Asia also comes with its own set of problems, like a quickly growing divide between rural and urban incomes, environmental degradation and new challenges for governance and institutions, according to the FAO.